Influence of River Water and Treated Industrial Sewage Water Quality on Compressive Strength of Concrete with Sawdust Ash as Partial Replacement of Cement
Keywords:
Water sample , Compressive Stregnth , Saw dust , Portable Water , River Water Environment , Chemical Impurities , Industrial Waste waterAbstract
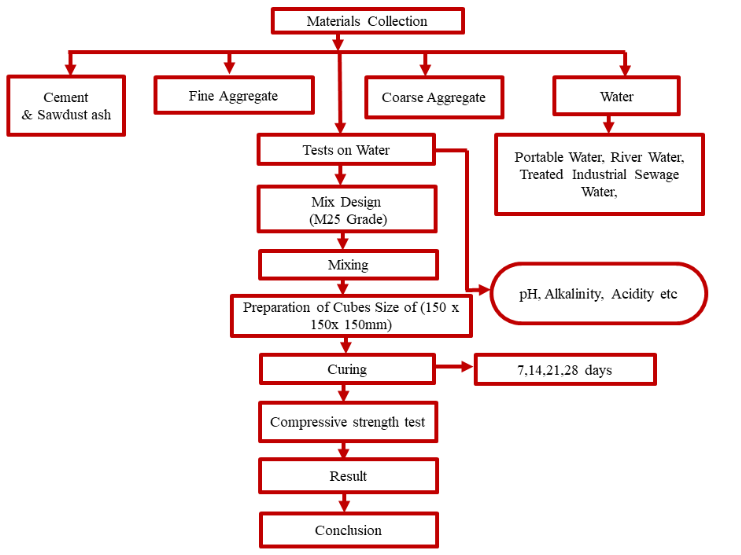
The study centered on the effect of different qualities of water on concrete compressive strength. The concrete mix of M25 grade with a water-cement ratio of 0.45 was investigated. Water samples, such as portable water, river water, and treated industrial sewage water were collected from Hassan city and were used to cast 150x150x150mm concrete cubes. The cured cubes were crushed on 7, 14, 21 & 28 days for compressive strength estimation. The results showed that the compressive strength of the concrete cubes made with portable water, river water, and treated industrial sewage water increased with days & not have many variations in their compressive strength The optimum replacement ratio was about 12%. This may be considered a solution not only to the problem of the environment but also to the problem of economics in the design of buildings. the combination of treated wastewater and saw dust ash greatly influences the compression strength of the concrete. The aim of the present study was to know the effect of chemical impurities in mixing different types of water on the compressive strength of concrete.
Downloads
References
Abrams, Saw Dust Ash as a Partial Replacement of Cement in Concrete'' International Journal For Scientific Research and Development.
Lea, Study on effect of different of water on compressive strength of concrete”
Mc Coy, International journal of research in Engg Study of water quality.
C.MARTHONG” ''Saw dust Ash as a Partial Replacement of Cement'', International Journal of Engineering Research & Applications, August 2012.
Ratod Vinod Kumar1 , M. Shiva RamaKrishna2, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
Steinour, Study of compressive strength of concrete cubes, P.Ghosh, Sawdust Ash as Concrete Material. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering. ASCE, Vol.
G.ReddyBabuEt.Al, Characteristics of Wood ASH/OPC Concrete. Leonardo Electron J Pract Technol.
Lakshmi & Chandran” Study on light weight mortars made of wood waste materials, Advanced material research 548, 34-41, 2012.
Barathan & gobinath, 'Saw dust Ash as a Partial Replacement of Cement.
Shetty, M.S.Concrete technology – Theory and Practice. 5th ed. S. Chand and Co. Ltd., RamNagar, New Delhi, India, 2004.
IS-456 - 2000-Plain and Reinforced Concrete Code of Practice [12] IS-516-1959 -Methods of tests for Strength of concrete.
IS-12269 - 1987- Specifications for 53 grade OPC.
IS 2386 (Part 1, 3 & 4) - 1963, Method of testing of aggregates for concrete.
IS 1199-1959 - Method of sampling and analysis of concrete.
IS 7320-1974 - Specification for concrete slump test apparatus .
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Ms.Bandhavya G B Gowda

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright on any article in the International Journal of Engineering and Applied Physics is retained by the author(s) under the Creative Commons license, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction provided the original work is properly cited.
License agreement
Authors grant IJEAP a license to publish the article and identify IJEAP as the original publisher.
Authors also grant any third party the right to use, distribute and reproduce the article in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ms.Bandhavya G B Gowda, Prashath S, Sandeep K, Bindhushree G B, Optimizing Green Concrete Brick Production with Rice Husk and Glass Waste: A Path to Sustainable Building , International Journal of Engineering and Applied Physics: Vol. 4 No. 3: September 2024
- Ms.Bandhavya G B Gowda, An Influence of Recycled Concrete Aggregate and Treated Waste Water Containing 50% GGBS Content in Light weight Concrete Mixes , International Journal of Engineering and Applied Physics: Vol. 4 No. 1: January 2024














