On the Dynamics and Heat Transfer of a Conducting Droplet during Electrospraying in the Dripping Mode
Keywords:
Electric Field, Electrospray, Heat Transfer, Dripping Regime, Conducting LiquidAbstract
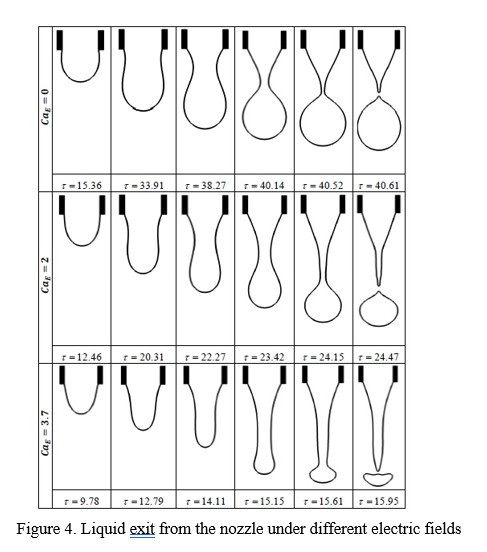
In this study, the influence of an applied electric field on the hydrodynamic and heat transfer of a conducting liquid exiting from a nozzle in the dripping regime is investigated. The flow and energy equations along with the electrostatic equations are solved to simulate this problem. The sharp formulation of the level set technique is implemented to capture the interface accurately. Subjected to an electric field, the liquid is exited faster and its elongation before detachment of the droplet is increased. Also, after the first droplet detaches, the liquid returns towards the nozzle. The length of the exited liquid after returning towards the nozzle increases under an electric field. Therefore, under electric stresses, the droplet formation occurs faster due to the rapid exit and more elongation of the liquid. Also, the size of the formed droplet is reduced with electric field intensity. Under an electric field, the heat transfer rate enhances rapidly in a short time interval before droplet detachment. The total heat transferred to the liquid exited from the nozzle is reduced by increasing the electric field intensity.
Downloads
References
K. Sung and C. S. Lee, "Factors Influencing Liquid Breakup in Electrohydrodynamic Atomization," Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 96, pp. 3956–3961, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1790062
A. K. Sen, et al., "Modeling and Characterization of a Carbon Fiber Emitter for Electrospray Ionization," Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, vol. 16, pp. 620, 2006.
R. T. Collins, et al., "Breakup of Electrified Jets," Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 588, pp. 75-129, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112007007409
L. K. Lim, et al., "Numerical Simulation of Cone?jet Formation in Electrohydrodynamic Atomization," AIChE Journal, vol. 57, pp. 57-78, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12254
B. V. Hokmabad, et al., "Electric Field-assisted Manipulation of Liquid Jet and Emanated Droplets," International Journal of Multiphase Flow, vol. 65, pp. 127-137, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2014.03.009
R. Kamali and M. K. Dehghan Manshadi, "Numerical Simulation of the Leaky Dielectric Microdroplet Generation in Electric Fields," International Journal of Modern Physics. C, vol. 27, pp. 1650012, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183116500121
M. P. Borthakur, et al., "Dynamics of Drop Formation from Submerged Orifices under the Influence of Electric Field," Physics of Fluids, vol. 30, pp. 30, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5063913
J. Rosell-Llompart, et al., "Electrosprays in the Cone-jet Mode: From Taylor Cone Formation to Spray Development," Journal of Aerosol Science., vol. 125, pp. 2-31, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2018.04.008
L. Guo, et al., "Charged Satellite Drop Avoidance in Electrohydrodynamic Dripping," Micromachines, vol. 10, pp. 172, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10030172
Z. Wang, et al., "Formation of Mono-dispersed Droplets with Electric Periodic Dripping Regime in Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) Atomization," Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, vol. 28, pp. 1241-1249, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.03.008
A. Panahi, et al., "Experimental Investigation of Electrohydrodynamic Modes in Electrospraying of Viscoelastic Polymeric Solutions," Physics of Fluids, vol. 32, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5132556
Z. Wang, et al., "Dynamics of Droplet Formation with Oscillation of Meniscus in Electric Periodic Dripping Regime," Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, vol. 120, pp. 110250, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2020.110250
J. Y. Kim and J. G. Hong, "Effect of Electrical Conductivity on Atomization Characteristics of Electrospray," Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, vol. 15, pp. 1427-1436, 2022. https://doi.org/10.47176/jafm.15.05.1094
D. S. Hathi, et al., "A Numerical Study on Breakup of a Liquid Jet in an Axial Electric Field," Journal of Aerosol Science, vol. 170, pp. 106142, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2023.106142
H. Nazari and P. Pournaderi, "The Electric Field Effect on the droplet Collision with a Heated Surface in the Leidenfrost Regime," Acta Mechanica, vol. 230, pp. 787-804, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2323-z
M. Kang, et al., "A Boundary Condition Capturing Method for Multiphase Incompressible Flow," Journal of Scientific Computing, vol. 15, pp. 3230360, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011178417620
M. Shen and B. Q. Li, "A 3D Conservative Level set Model to Simulate Drop Impact with Phase Change onto Solid Surfaces," International Journal of Multiphase Flow, vol. 169, pp. 104615, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2023.104615
M. Emdadi and P. Pournaderi, "Study of Droplet Impact on a Wall Using a Sharp Interface Method and Different Contact Line Models," Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, vol. 12, pp. 1001-1012, 2019. https://doi.org/10.29252/JAFM.12.04.29029
R. Khanpour and P. Pournaderi, "Simulation of the Liquid Spraying Process in the Dripping Mode by Using the Level-Set Method," Amirkabir Journal of Mechanical Engineering, vol. 52, pp. 847-862, 2019. https://doi.org/10.22060/mej.2019.14689.5914
H. Nazari and P. Pournaderi, "Simulation of Hydrodynamic Behavior of a Conductive Drop under an Electric Field," Amirkabir Journal of Mechanical Engineering, vol. 51, pp. 297-312, 2019. https://doi.org/10.22060/mej.2017.12700.5400
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Reza Khanpour, Pedram Pournaderi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright on any article in the International Journal of Engineering and Applied Physics is retained by the author(s) under the Creative Commons license, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction provided the original work is properly cited.
License agreement
Authors grant IJEAP a license to publish the article and identify IJEAP as the original publisher.
Authors also grant any third party the right to use, distribute and reproduce the article in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Farshid Narges-Moghadam, Pedram Pournaderi, Free Convection Heat Transfer of Alumina-Water Nanofluid in an Enclosure: Assessment of Viscosity and Conductivity Models , International Journal of Engineering and Applied Physics: Vol. 2 No. 1: January 2022














